America’s stock market is shrinking

Imagine it or not, the U.S. stock market place experienced way far more organizations again when Mark McGwire was chasing homerun documents.
The amount of publicly outlined U.S. shares peaked at a document seven,562 for the duration of McGwire’s file-placing summer season of 1998, according to the Wilshire 5000 Total Market place Index. Right now, there are just 3,812.
So what offers? Just place, there are much more organizations disappearing than coming into the inventory industry.
This just isn’t a trivial difficulty that only issues to bankers on Wall Street. Not only do investors have less alternatives to commit in, but it immediately impacts American positions.
“We are shrinking the stock marketplace. Unless of course we determine out how to generate a whole lot much more startups and a great deal more IPOs, the economic system is going to proceed to create employment at lower costs than it should,” stated David Weild, former vice chairman at Nasdaq who has testified in Congress about money markets.
How did we get right here? It’s important to observe that the collective worth — identified as industry capitalization — of the stock industry has risen tremendously considering that the nineties. However, the variety of stocks in the marketplace peaked in July 1998, just as firms ended up racing to go public in the Internet growth.
“There was this myth that if you could begin a firm and set dot-com in the name you would turn out to be instantaneously abundant,” stated Bob Waid, controlling director of Wilshire Analytics, which oversees the Wilshire 5000.
Clearly, they had been mistaken. Heading out of business is one particular way firms get delisted from the industry.
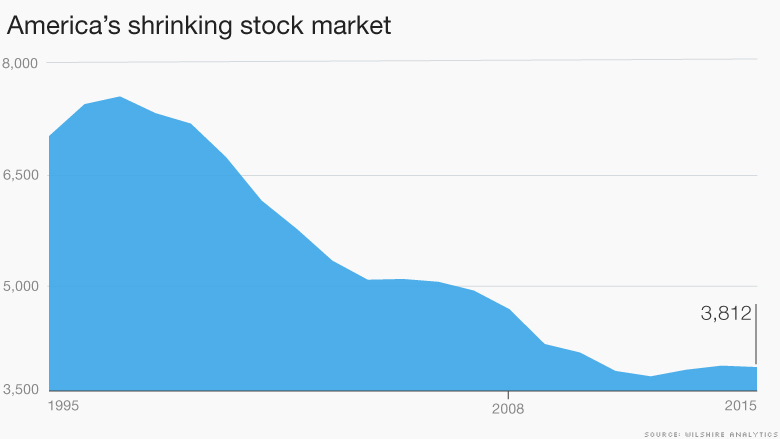
The number of shares in the Wilshire 5000 Complete Industry Index has collapsed in excess of the very last two decades.
Connected: IMF warns U.S.: Your fiscal method is (even now) vulnerable
IPOs are unable to hold up with M&A: The other way is via mergers and acquisitions, which cause 1 inventory to cease investing as it truly is absorbed by one more company. The M&A market is booming : A record $ one.one trillion of U.S. deals had been carried out throughout the initial fifty percent of 2015, according to Dealogic.
In a excellent world, delistings are offset by the development of new public businesses by means of IPOs, or first community choices. However the IPO marketplace has not rebounded to its dot-com period levels.
Again in 1996, an amazing 848 firms went public, boosting a total of $ seventy eight.6 billion, according to Dealogic. In 2014, the IPO industry did $ ninety six billion of bargains very last year, but only 292 firms went community.
One particular explanation for the IPO drop is the existence of other resources of cash, including undertaking capital and non-public-equity companies. Startups like Uber and Airbnb are raising gobs of money in the pre-IPO market, which some worry appears like a bubble .
Other startups may possibly be discouraged from going public by regulation. Costly disclosure and other needs in Sarbanes-Oxley have lessened the attraction of the IPO route.
Startup globe is shrinking, way too: The other clarification is that there are basically much less youthful companies in the U.S. Startups produced up virtually 15% of all U.S. organizations in 1978, in comparison with just eight% in 2011, according to Brookings Institute study .
“We have experienced a massive collapse in the variety of startups. That’s the place task development occurs,” mentioned Weild.
Weild blames main changes to marketplace structure in the late 1990s and early 2000s that have deprived small-cap stocks (like startups) in opposition to big-cap ones like IBM ( IBM , Tech30 ) and Microsoft ( MSFT , Tech30 ) .
For illustration, Nasdaq’s ( NDAQ ) choice to turn into a for-income corporation has shifted its objectives. Weild mentioned the exchange no for a longer time advocates for the ecosystem of tiny investment banks that formerly supported small-cap stocks.
Also, Regulation ATS in 1998 ushered in the common use of electronic markets in the U.S., producing investing far a lot more effective and less expensive for each day investors. Nonetheless, Weild argues it also made it much less lucrative for the little expenditure banking institutions, numerous of which no lengthier exist.
Venture exchanges: So what is the remedy? Weild and other individuals have pushed Congress to create so-named “enterprise exchanges” that would cater to younger organizations. In principle, these exchanges would help the economic climate by providing startups accessibility to capital that they aren’t getting from the current market framework.
“We’ve designed a market composition in the United States that’s actually undermined our future. If you shut down your capability to begin little companies, you also inhibit your capacity to produce massive types,” Weild mentioned.
Relevant: IMF suggests world economic climate will sluggish this yr
